ログアウトされました
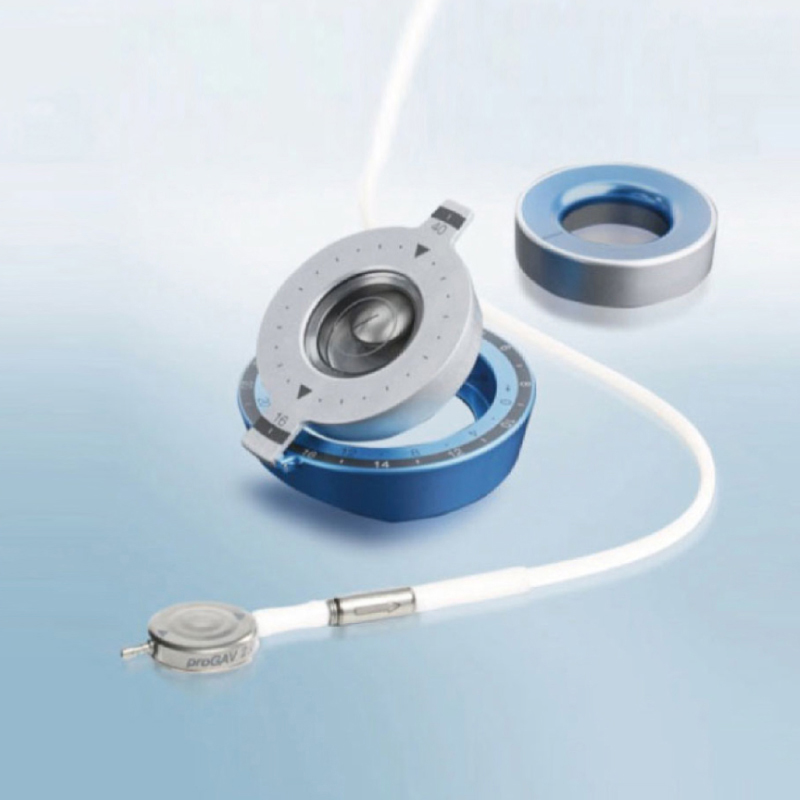
重力可変式バルブ
ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブ
シャント技術における課題は、姿勢に依存して変化する静水圧への
対応です。
医療従事者の確認
この先は、医療従事者の方を対象とした情報を提供しております。 大変申し訳ございませんが、医療従事者の方以外はご遠慮ください。
あなたは医療従事者ですか?
確認 はい、わたしは医療従事者です. キャンセル いいえ、わたしは医療従事者ではありません.
安心の設計
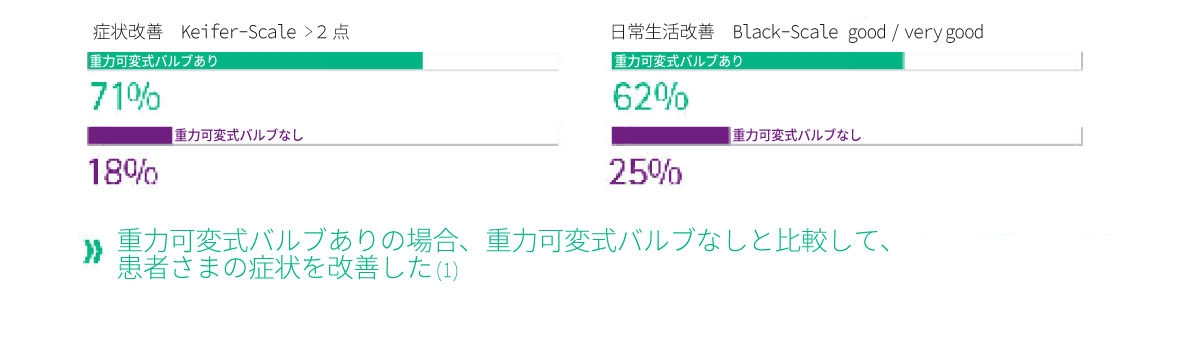
重力可変式バルブを使用した水頭症シャントシステムは、姿勢に依存する重力の影響を克服し、オーバードレナージの合併症を軽減し、良好な症状改善とオーバードレナージ関連不具合の大幅な減少という良好な結果を示しています。[1]
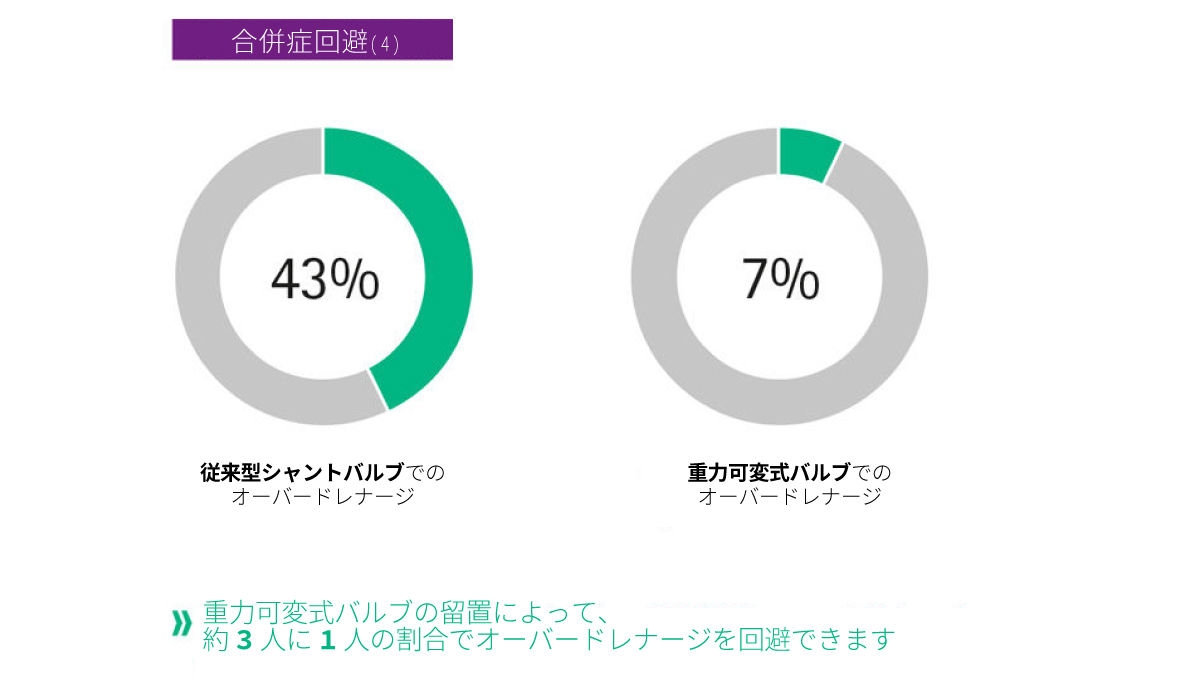
合併症と再建術の回避
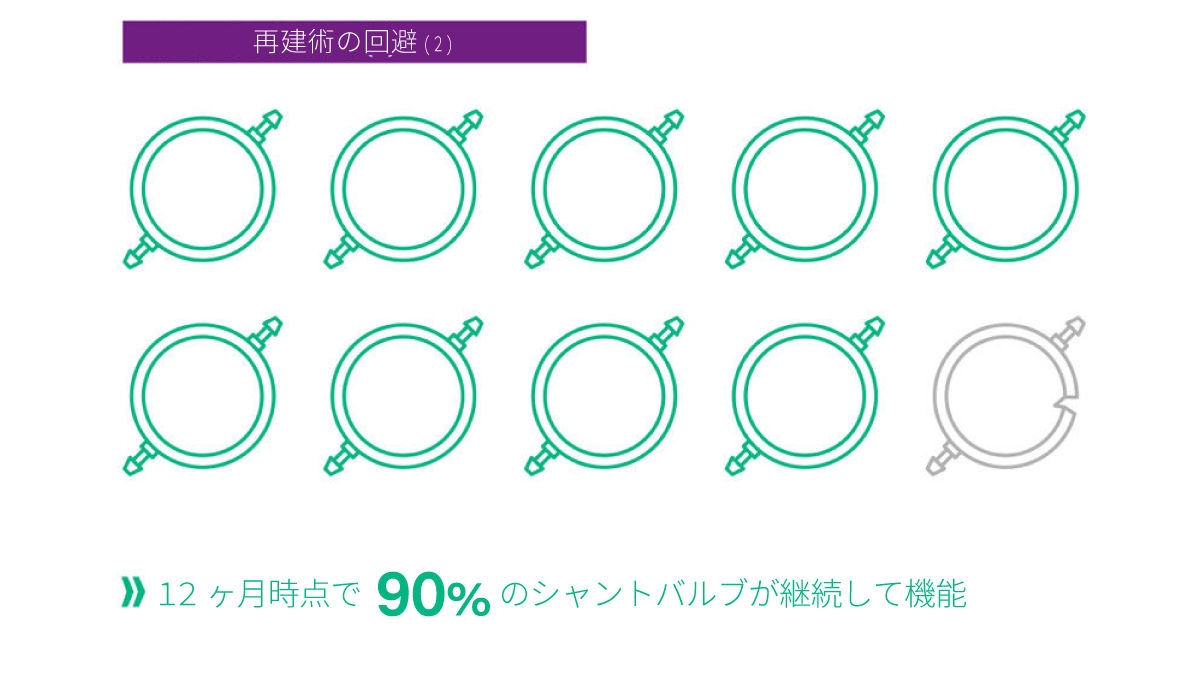
ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブは再建術のリスクを低下させることが臨床研究で分かっています。ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブは、すべての年齢層において、12ヶ月で90%[1]、2年以降で80%[2]といった長期間に渡って機能していることが示されています。成人よりも合併症の発生が多いとされる乳児においても長期にわたってシャントバルブが機能していることが観察されています[2]。さらに、従来のシャントバルブを使用した場合と比較して、オーバードレナージのリスクを36%低下させます。つまり、シャント手術を受ける患者さまの3人に1人の割合で、重力可変式バルブを使用することによりオーバードレナージの合併症を防ぐことができます。
機械的な故障の回避
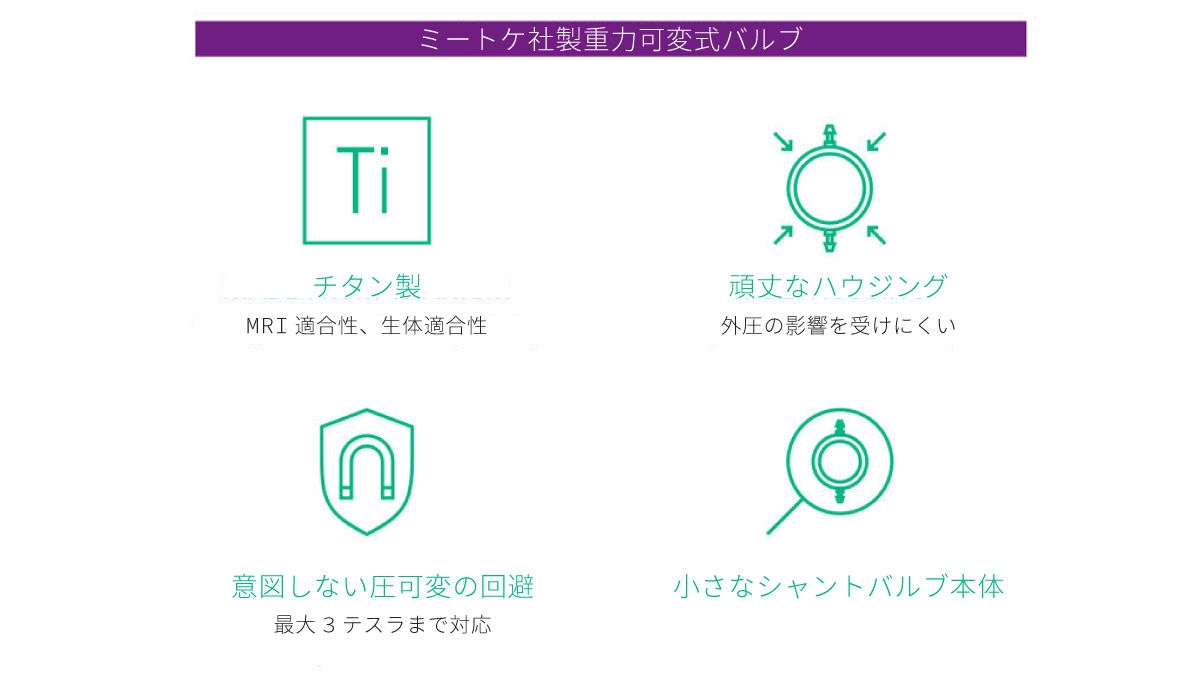
全てのミートケシャントバルブのハウジングはチタンで高精細に製造されています。強度の高いチタンのおかげで、シャントバルブは非常に小さいながらも内部の流路は最適化されています。頑丈なハウジングによって、チタン製シャントバルブは皮下で外圧による影響を受けません。チタンは生体適合性が高く、医療機器への使用に適していると考えられています[6]。また、チタンはMRI適合です。
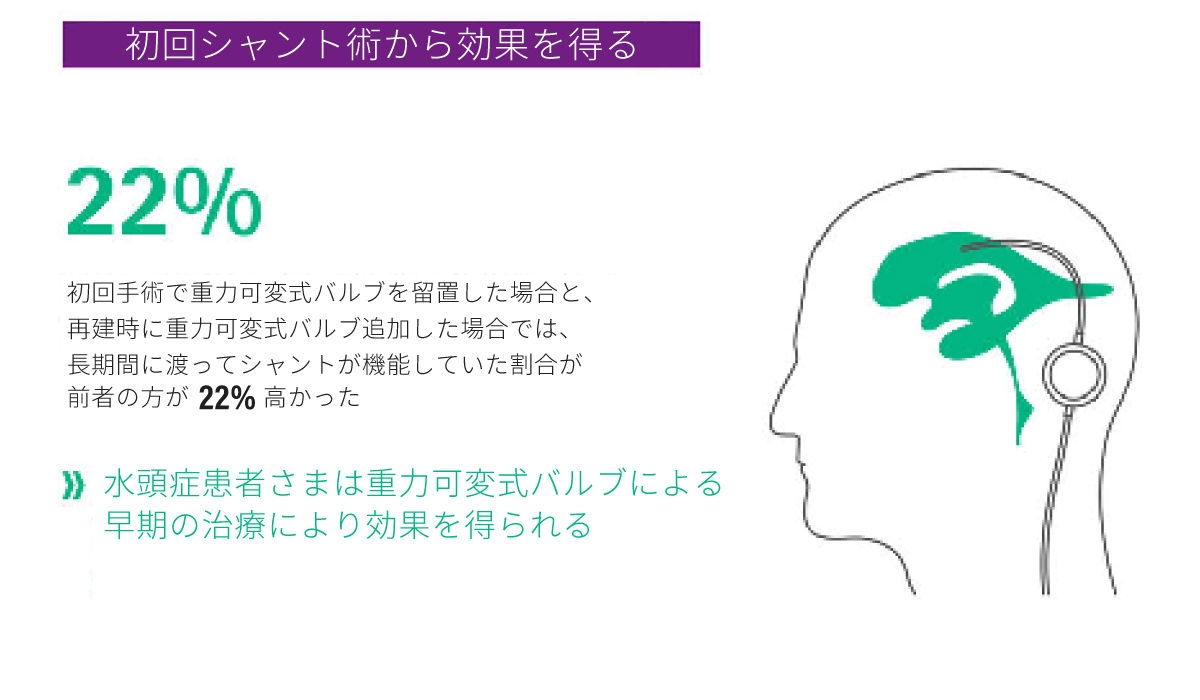
初回からよい治療を
わずか3ヶ月であっても[8]、治療の遅れは患者さまにとって有害であることが証明されています[7]。特に、脳が成長過程にある乳児では、最初に選択された水頭症治療と起こる可能性のある合併症が、長期的な症状改善に影響を与えます[9]。初回手術時に重力可変式バルブを留置された乳児と、再建術時に重力可変式バルブを追加された乳児では、初回手術時に留置された方が、長期間に渡ってシャントが機能していたことから[9]、初回の重要性が強調されています。水頭症の治療の遅れは悪影響をもたらす可能性があり、特に、不可逆的な合併症を考慮すると、早期の介入が必要です。初回治療から、利用可能な最善の治療法を選択することが重要です。
最適化 - 妥協しない
シャント技術における重要な課題は、姿勢に依存した静水圧の変化をいかに計算するかということです。[10] 重力可変式シャントバルブは、姿勢に依存した静水圧の変化を補正するため、オーバードレナージを防ぐことができます。[11] 臥位では、重力可変式バルブは完全に開放するため、全体的な流路抵抗には影響をしませんが、座位・立位では、流路抵抗は重力可変式バルブと差圧バルブの両方によって決定されます。臨床現場では、ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブと圧可変式バルブを使用することで、オーバードレナージやアンダードレナージによるシャント再建術の回数を減らすことができ [3] 、症状や全体的な日常機能を改善できることが示されているます。[10] さらに、重力可変式バルブは乳児の水頭症治療にも有効であることが示されています。[12]
ミートケ社製重力可変式バルブは、臥位での開放圧設定に影響を与えずに、オーバードレナージを相殺することができる。各患者さまの立位時および臥位時の最適な開放圧を、どちらかに妥協することなく設定することができる。
日常の磁力の影響
日常の低強度磁場によるシャントバルブ開放圧の意図しない変更は、患者さまにとっても医師にとっても大きな懸念事項です。しかし、シャントバルブが誤って変更されないと、どうすれば確信が持てるでしょうか?重要なポイントは、圧可変式バルブがMRI中に発生する強力な磁場から保護されているかどうかということでしょう。MRシステムという強い磁場が、圧可変式バルブに影響を与えないのであれば、日常の低強度磁場も影響を及ぼさないはずです。圧可変式のミートケ社製シャントバルブは、最大3テスラの磁場による影響から保護する「アクティブロック機構」を備えています。[13]
ミートケ社 関連情報
[1] Tschan CA, Antes S, Huthmann A, et al. Overcoming CSF overdrainage with the adjustable gravitational valve proSA. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2014;156(4):767-76; discussion 76.
[2] Sprung C, Schlosser HG, Lemcke J, et al. The adjustable proGAV shunt: a prospective safety and reliability multicenter study. Neurosurgery 2010;66(3):465-74.
[3] Gebert AF, Schulz M, Schwarz K, Thomale UW. Long-term survival rates of gravity-assisted, adjustable differential pressure valves in infants with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2016 17:544-551
[4] Lemcke J, Meier U, Müller C, Fritsch M, Kehler U, Langer N et al. Safety and efficacy of gravitational shunt valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a pragmatic, randomised, open label, multicentre trial (SVASONA). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2013 84(8):850-857
[5] Thomale UW, Gebert AF, Haberl H, et al. Shunt survival rates by using the adjustable differential pressure valve combined with a gravitational unit (proGAV) in pediatric neurosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 2013;29(3):425-31.
[6] Lemcke J, Meier U, Muller C, et al. Safety and efficacy of gravitational shunt valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a pragmatic, randomised, open label, multicentre trial (SVASONA). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2013;84(8):850-7.
[7] Sidambe AT. Biocompatibility of Advanced Manufactured Titanium Implants-A Review. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) 2014;7(12):8168-88.
[8] Saini M, Singh Y, Arora O, et al. Implant biomaterials: A comprehensive review. World journal of clinical cases 2015;3(1):52-7.
[9] Toma AK, Watkins LD. Surgical management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a trial of a trial. Br J Neurosurg 2016;30(6):605.
[10] Toma AK, Stapleton S, Papadopoulos MC, et al. Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurg Rev 2011;34(4):433-9.
[11] Irving G, Neves AL, Dambha-Miller H, et al. International variations in primary care physician consultation time: a systematic review of 67 countries. BMJ Open 2017;7(10):e017902.
[12] Suchorska B, Kunz M, Schniepp R, et al. Optimized surgical treatment for normal pressure hydrocephalus: comparison between gravitational and differential pressure valves. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2015;157(4):703-9.
[13] Chari A, Czosnyka M, Richards HK, Pickard JD, Czosnyka ZH. Hydrocephalus shunt technology: 20 years of experience from the Cambridge Shunt Evaluation Laboratory, J Neurosurg 2014;120(3): 697-707.






